$densify (aggregation)
Definition
$densifyNew in version 5.1.
Creates new documents in a sequence of documents where certain values in a field are missing.
You can use
$densifyto:Fill gaps in time series data.
Add missing values between groups of data.
Populate your data with a specified range of values.
Syntax
The $densify stage has this syntax:
{ $densify: { field: <fieldName>, partitionByFields: [ <field 1>, <field 2> ... <field n> ], range: { step: <number>, unit: <time unit>, bounds: < "full" || "partition" > || [ < lower bound >, < upper bound > ] } } }
The $densify stage takes a document with these fields:
Field | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|
Required | The field to densify. The values of the specified
Documents that do not contain the specified To specify a For restrictions, see | |
Optional | The set of fields to act as the compound key to group
the documents. In the If you omit this field, For an example, see Densifiction with Partitions. For restrictions, see | |
Required | An object that specifies how the data is densified. | |
Required | You can specify
If
If
If
| |
Required | The amount to increment the field value
in each document. If range.unit is specified, | |
Required if field is a date. | The unit to apply to the step field when incrementing date values in field. You can specify one of the following values for
For an example, see Densify Time Series Data. |
Behavior and Restrictions
field Restrictions
For documents that contain the specified field,
$densify errors if:
Any document in the collection has a
fieldvalue of type date and the unit field is not specified.Any document in the collection has a
fieldvalue of type numeric and the unit field is specified.The
fieldname begins with$. You must rename the field if you want to densify it. To rename fields, use$project.
partitionByFields Restrictions
$densify errors if any field name in the
partitionByFields array:
Evaluates to a non-string value.
Begins with
$.
range.bounds Behavior
If range.bounds is an array:
Order of Output
$densify does not guarantee sort order of the documents
it outputs.
To guarantee sort order, use $sort on the field you want
to sort by.
Examples
Densify Time Series Data
Create a weather collection that contains temperature readings over
four hour intervals.
db.weather.insertMany( [ { "metadata": { "sensorId": 5578, "type": "temperature" }, "timestamp": ISODate("2021-05-18T00:00:00.000Z"), "temp": 12 }, { "metadata": { "sensorId": 5578, "type": "temperature" }, "timestamp": ISODate("2021-05-18T04:00:00.000Z"), "temp": 11 }, { "metadata": { "sensorId": 5578, "type": "temperature" }, "timestamp": ISODate("2021-05-18T08:00:00.000Z"), "temp": 11 }, { "metadata": { "sensorId": 5578, "type": "temperature" }, "timestamp": ISODate("2021-05-18T12:00:00.000Z"), "temp": 12 } ] )
This example uses the $densify stage to fill in the gaps
between the four-hour intervals to achieve hourly granularity for the
data points:
db.weather.aggregate( [ { $densify: { field: "timestamp", range: { step: 1, unit: "hour", bounds:[ ISODate("2021-05-18T00:00:00.000Z"), ISODate("2021-05-18T08:00:00.000Z") ] } } } ] )
In the example:
The
$densifystage fills in the gaps of time in between the recorded temperatures.field: "timestamp"densifies thetimestampfield.range:step: 1increments thetimestampfield by 1 unit.unit: hourdensifies thetimestampfield by the hour.bounds: [ ISODate("2021-05-18T00:00:00.000Z"), ISODate("2021-05-18T08:00:00.000Z") ]sets the range of time that is densified.
In the following output, the $densify stage fills in the gaps of time
between the hours of 00:00:00 and 08:00:00.
[ { _id: ObjectId("618c207c63056cfad0ca4309"), metadata: { sensorId: 5578, type: 'temperature' }, timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T00:00:00.000Z"), temp: 12 }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T01:00:00.000Z") }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T02:00:00.000Z") }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T03:00:00.000Z") }, { _id: ObjectId("618c207c63056cfad0ca430a"), metadata: { sensorId: 5578, type: 'temperature' }, timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T04:00:00.000Z"), temp: 11 }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T05:00:00.000Z") }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T06:00:00.000Z") }, { timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T07:00:00.000Z") }, { _id: ObjectId("618c207c63056cfad0ca430b"), metadata: { sensorId: 5578, type: 'temperature' }, timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T08:00:00.000Z"), temp: 11 } { _id: ObjectId("618c207c63056cfad0ca430c"), metadata: { sensorId: 5578, type: 'temperature' }, timestamp: ISODate("2021-05-18T12:00:00.000Z"), temp: 12 } ]
Densifiction with Partitions
Create a coffee collection that contains data for two
varieties of coffee beans:
db.coffee.insertMany( [ { "altitude": 600, "variety": "Arabica Typica", "score": 68.3 }, { "altitude": 750, "variety": "Arabica Typica", "score": 69.5 }, { "altitude": 950, "variety": "Arabica Typica", "score": 70.5 }, { "altitude": 1250, "variety": "Gesha", "score": 88.15 }, { "altitude": 1700, "variety": "Gesha", "score": 95.5, "price": 1029 } ] )
Densify the Full Range of Values
This example uses $densify to densify the
altitude field for each coffee variety:
db.coffee.aggregate( [ { $densify: { field: "altitude", partitionByFields: [ "variety" ], range: { bounds: "full", step: 200 } } } ] )
The example aggregation:
Partitions the documents by
varietyto create one grouping forArabica Typicaand one forGeshacoffee.Specifies a
fullrange, meaning that the data is densified across the full range of existing documents for each partition.Specifies a
stepof200, meaning new documents are created ataltitudeintervals of200.
The aggregation outputs the following documents:
[ { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480475"), altitude: 600, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 68.3 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480476"), altitude: 750, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 69.5 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 800 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480477"), altitude: 950, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 70.5 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 600 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 800 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1000 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1200 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480478"), altitude: 1250, variety: 'Gesha', score: 88.15 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1400 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1600 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480479"), altitude: 1700, variety: 'Gesha', score: 95.5, price: 1029 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 1000 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 1200 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 1400 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 1600 } ]
This image visualizes the documents created with $densify:
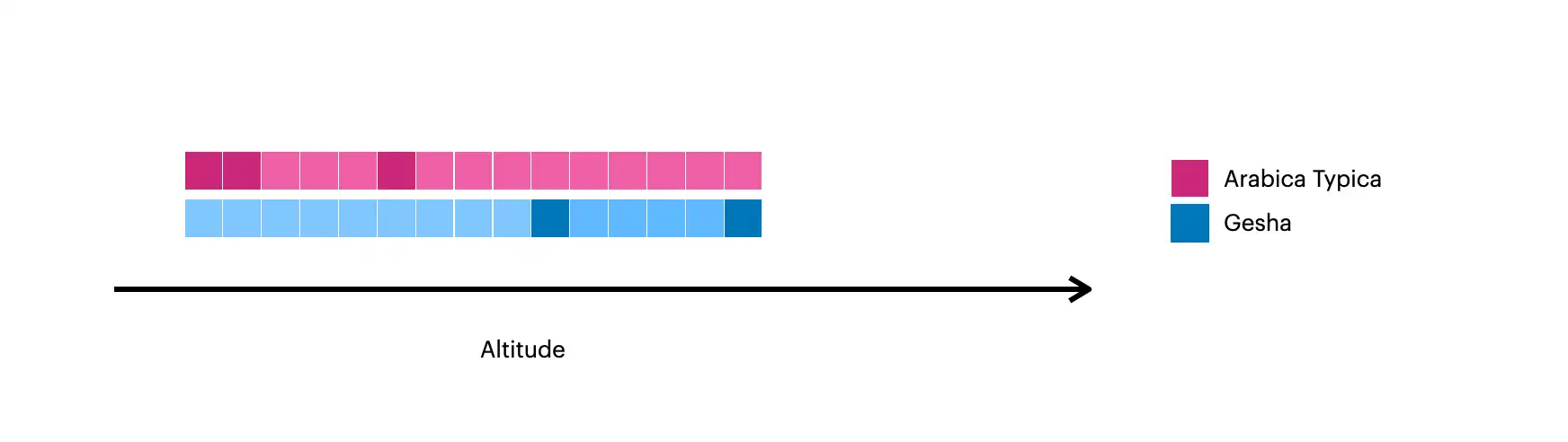
The darker squares represent the original documents in the collection.
The lighter squares represent the documents created with
$densify.
Densify Values within Each Partition
This example uses $densify to only densify gaps in the
altitude field within each variety:
db.coffee.aggregate( [ { $densify: { field: "altitude", partitionByFields: [ "variety" ], range: { bounds: "partition", step: 200 } } } ] )
The example aggregation:
Partitions the documents by
varietyto create one grouping forArabica Typicaand one forGeshacoffee.Specifies a
partitionrange, meaning that the data is densified within each partition.For the
Arabica Typicapartition, the range is600-950.For the
Geshapartition, the range is1250-1700.
Specifies a
stepof200, meaning new documents are created ataltitudeintervals of200.
The aggregation outputs the following documents:
[ { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480475"), altitude: 600, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 68.3 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480476"), altitude: 750, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 69.5 }, { variety: 'Arabica Typica', altitude: 800 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480477"), altitude: 950, variety: 'Arabica Typica', score: 70.5 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480478"), altitude: 1250, variety: 'Gesha', score: 88.15 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1450 }, { variety: 'Gesha', altitude: 1650 }, { _id: ObjectId("618c031814fbe03334480479"), altitude: 1700, variety: 'Gesha', score: 95.5, price: 1029 } ]
This image visualizes the documents created with $densify:
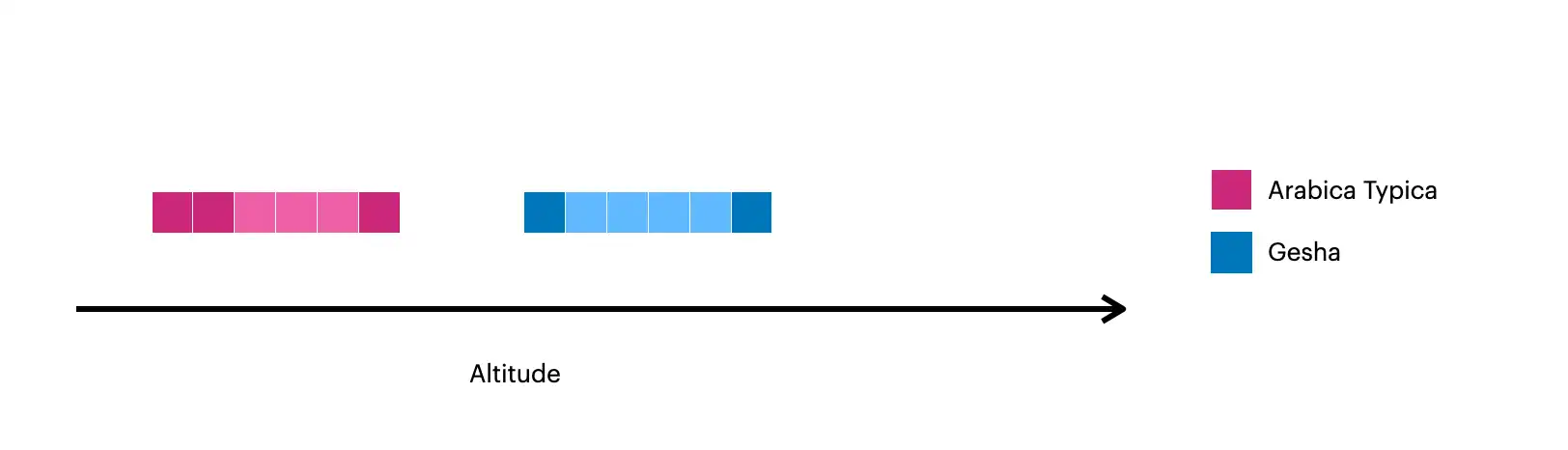
The darker squares represent the original documents in the collection.
The lighter squares represent the documents created with
$densify.